By U6062766
My work experience was held at the ACT Parks and Conservation Services (PCS) Athllon Depot. It involved reviewing, synthesising and condensing information from the Offset Management Plans of Isaacs Ridge Nature Reserve Extension and Kenny Nature Reserve into summaries. These summaries would then be used to track management obligations and to create future management plans. This work experience was obtained under the guidance of Karen Ikin, who is Conservation Planner in the Environmental Offsets.

What is a biodiversity offset?
Habitat loss and fragmentation are key threats to biodiversity. A biodiversity offset is a policy instrument proposed and utilised by developers and planners for compensating for the loss of biodiversity in one place by biodiversity gains in another. Offsetting allows more flexibility for developers and regulators to continue with development with no net loss of biodiversity. Additionally, it places an economic value on biodiversity equivalent to the cost of the offset.
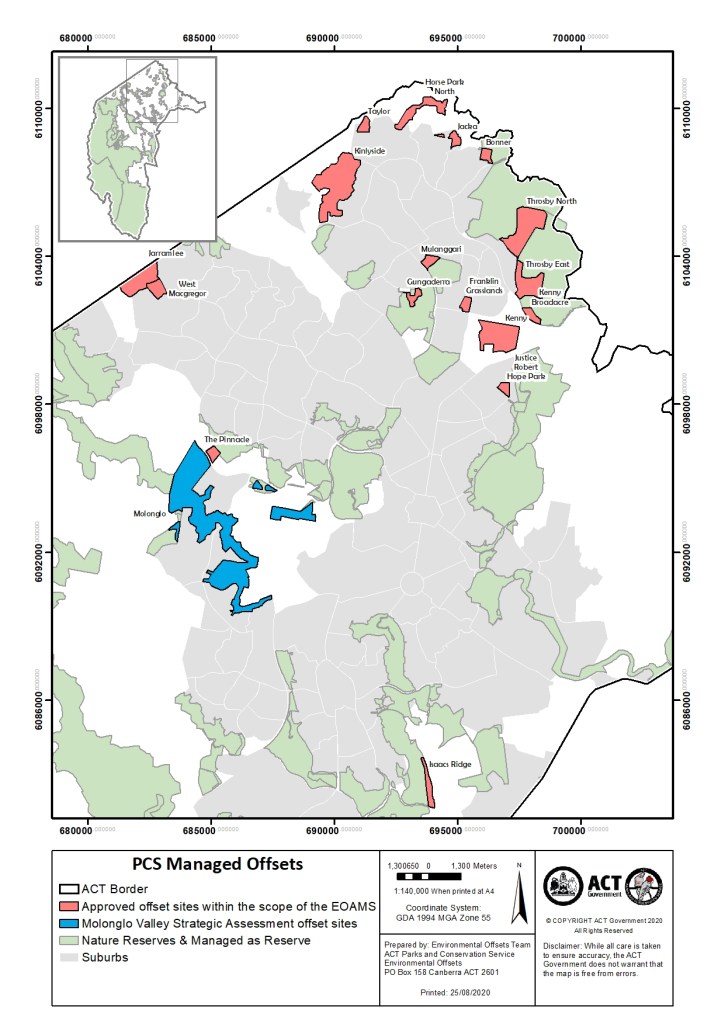
Offset site 1: Isaacs Ridge Nature Reserve Extension
Is a planned biodiversity offset for the Mugga Lane Resources Management Centre Expansion, which involved clearing ~9.5 ha of vegetation consistent with White Box-Yellow Box -Blakely’s Red Gum Grassy Woodland. This environment is listed as critically endangered under the EPBC Act 1999 and endangered under the ACT Nature Conservation Act 2011. This ecosystem was consistent with the land nearby Isaacs Ridge Nature Reserve which is part of a large contiguous wooded vegetation corridor. ACT NOWaste is proactively managing the area targeting Matters of National Significance (MNES) affected by the expansion of the project. The primary objective of the offset is to protect and enhance the condition of the White Box- Yellow Box Blakey’s Red Gum.


Offset site 2: Kenny Nature Reserve
Is biodiversity offset under the Gungahlin Strategic Assessment Biodiversity Plan, which has been developed as a result of urban development that has impacted ~173 ha of MNES Habitat, including the Striped Legless Lizard (Delma impar) and Box Gum Woodland. The offset site is located in a nature reserve in the south-west of the suburb Kenny. The primary goal of the offset is to retain ~90% of striped legless lizard population and the majority of box gum woodland, ~300-year-old large trees. Other MNES in the area include the Superb Parrot (Polytelis swainsonii) and the Golden Sun Moth (Synemon plana). Management of a nature reserve in Kenny has been ongoing before the commencement of construction.
Work experience project
The project involved documenting threatened species and ecological community’s management of offset sites for the development of future management plans. Activities included reading through the Isaacs Ridge Nature Reserve Extension Offset Management Plan and the Gungahlin Strategic Assessment Biodiversity Plan, extracting, collating and summarising information into categories of types of MNES, offset description, outcomes and mechanism for implementation into a table on Excel. Additionally, assessing the vegetation zones of each site. These would assist the offset team to easily locate and compare the outlines of the management plan against what is actually being done in the field which will be of assistance when updating versions of both management plans.
Personal conclusion
Biodiversity offsets are a valuable tool for moderating development whilst maintaining protection of biodiversity. This work experience has proved to be both an eye-opening and hands-on experience into understanding the amount of research and time that goes into creating and managing offset sites. The dedication and passion of the offset team provided to be a good work environment.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Karen Ikin for incorporating me into her busy schedule, for facilitating this work experience and welcoming me into her work space.
